The Anatolian hypothesis, also known as the Anatolian theory or the sedentary farmer theory, first developed by British archaeologist Colin Renfrew in 1987, proposes that the dispersal of Proto-Indo-Europeans originated in Neolithic Anatolia.
- What was Colin Renfrew theory?
- What is the Anatolian hearth theory?
- What is the Kurgan hearth theory?
- What is the Paleolithic Hypothesis?
- What are the Kurgan and Anatolian heart theories?
- What is the war hypothesis of language diffusion?
- Did anyone actually speak Proto Indo-European?
- What is the conquest theory?
- What is the Indo-European hypothesis?
- What are the two competing hypotheses about the origin and diffusion of the Proto Indo-European language?
- What present day country did the Anatolian hearth theory originate from?
- Where did the Kurgans come from?
- Which theory of language diffusion believed we first came out of Anatolia down to Iran into India around the Caspian Sea and into Europe?
- What are the 3 main characteristics of Paleolithic Age?
- What are Paleolithic vegetables?
- What is the agricultural theory of language diffusion?
- Was Indo-European diffused by nomadic warriors or sedentary farmers?
- What is the best example of the diffusion of a language?
- What hypothesis has Marija Gimbutas contributed to?
- Who are Kurgan people?
- How did the Kurgan theory spread?
- What is an example of conquest theory?
- What is linguistic hearth?
- How did English become widely diffused?
- Is Chinese an Indo-European language?
- Is Latin a proto language?
- Is Arabic Indo-European?
- Who first proposed the Indo-European hypothesis?
- How does the Anatolian hearth theory say the Indo-European family originated and diffused?
What was Colin Renfrew theory?
This theory was proposed by British scholar Colin Renfrew on the diffusion of Proto-Indo-European and agriculture that states that three areas in and near the first agricultural hearth, the Fertile Crescent, that each gave rise to a major language family.
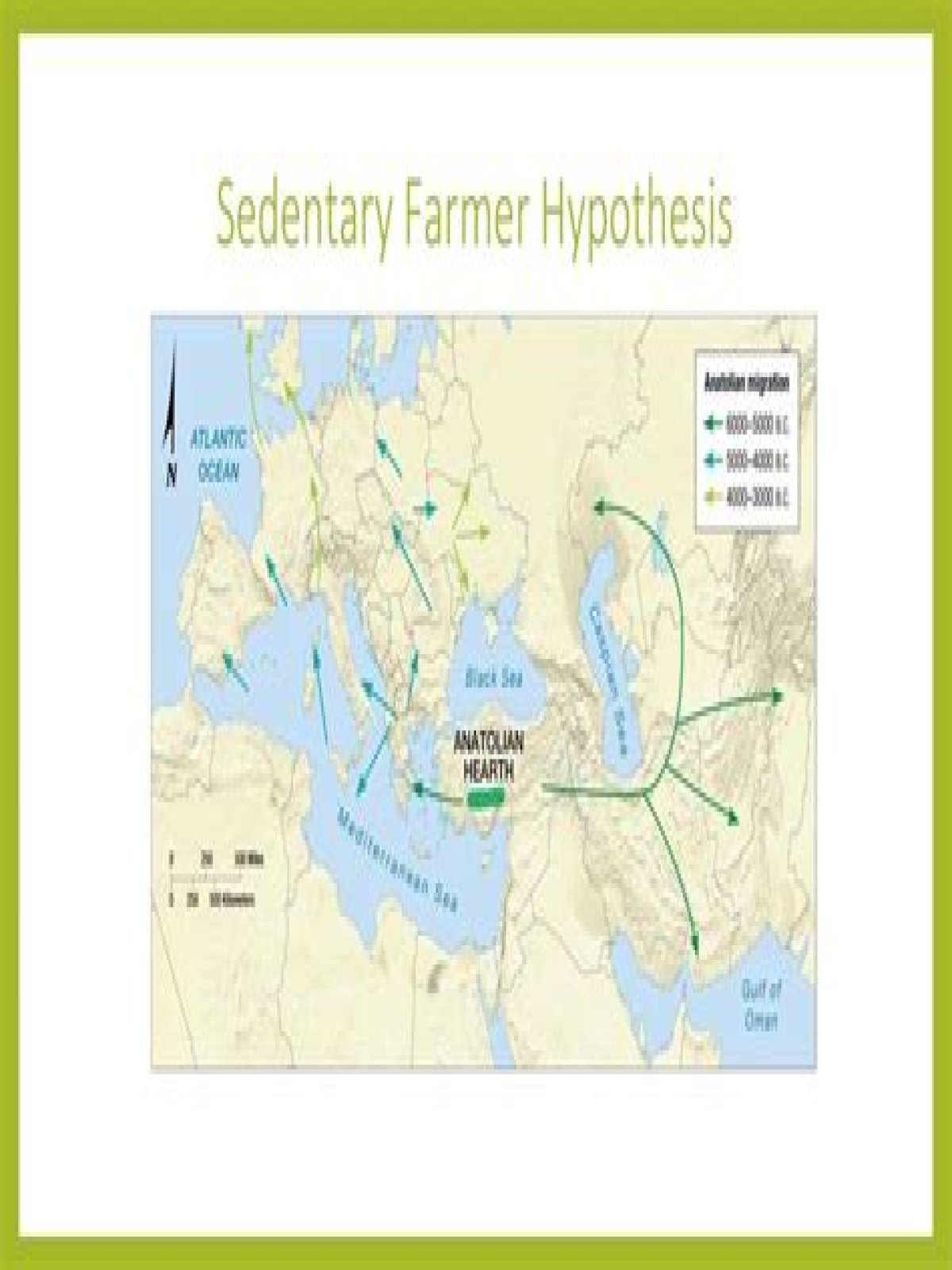
What is the Anatolian hearth theory?
Anatolian Hearth Theory. Theory of how language first began to diffuse. According to this theory, Indo-European diffused along with agricultural innovations west into Europe and east into Asia.
What is the Kurgan hearth theory?
It postulates that the people of a Kurgan culture in the Pontic steppe north of the Black Sea were the most likely speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). The term is derived from the Russian kurgan (курга́н), meaning tumulus or burial mound.What is the Paleolithic Hypothesis?
The Paleolithic continuity paradigm (or PCP, before 2010 also Paleolithic continuity theory or PCT), is a hypothesis suggesting that the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) can be traced back to the Upper Paleolithic, several millennia earlier than the Chalcolithic or at the most Neolithic estimates in other scenarios …
What are the Kurgan and Anatolian heart theories?
The Kurgan theory centres on possible archaeological evidence for an expansion into Europe and the Near East by Kurgan horsemen beginning in the sixth millennium BP. In contrast, the Anatolian theory claims that Indo-European languages expanded with the spread of agriculture from Anatolia around 8,000-9,500 years bp.
What is the war hypothesis of language diffusion?
The theory that the first Proto-Indo-European speakers were Kurgans, who conquered much of Europe and South Asia between 3500 and 2500 B.c, diffusing their language through war and conquest. You just studied 26 terms!
Did anyone actually speak Proto Indo-European?
No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists. … PIE is hypothesized to have been spoken as a single language from 4500 BC to 2500 BC during the Late Neolithic to Early Bronze Age, though estimates vary by more than a thousand years.What is the conquest theory?
Conquest theory is when a person or a group of people take control of an area and make everyone in that area follow their rules and beliefs.
What is steppe hypothesis?This article provides new support for the “steppe hypothesis” or “Kurgan hypothesis”, which proposes that Indo-European languages first spread with cultural developments in animal husbandry around 4500 – 3500 BCE.
Article first time published onWhat is the Indo-European hypothesis?
The hypothesis suggests that the Indo-Europeans, a patriarchal, patrilinear, and nomadic culture of the Pontic–Caspian steppe (now part of Eastern Ukraine and Southern Russia), expanded in several waves during the 3rd millennium BC, coinciding with the taming of the horse.
What are the two competing hypotheses about the origin and diffusion of the Proto Indo-European language?
There are two competing hypotheses for the origin of the Indo-European language family. The conventional view places the homeland in the Pontic steppes approximately 6kya. An alternative hypothesis claims the languages spread from Anatolia with the expansion of farming 8–9.5kya.
What present day country did the Anatolian hearth theory originate from?
The agriculture theory states that the hearth was in Anatolia (Turkey – >10,000 yrs. ago); the Proto-Indo-European language diffused directly westward across the Aegean Sea into the Balkans, to Italy, and northward across the plains of Europe into Scandinavia and the British Isles.
Where did the Kurgans come from?
Originally in use on the Pontic–Caspian steppe, kurgans spread into much of Central Asia and Eastern, Southeast, Western and Northern Europe during the 3rd millennium BC.
Which theory of language diffusion believed we first came out of Anatolia down to Iran into India around the Caspian Sea and into Europe?
The most popular hypothesis for the origin and spread of the language is the Kurgan hypothesis, which postulates an origin in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of Eastern Europe.
What are the 3 main characteristics of Paleolithic Age?
- The inhabitants were dependent on their environment. Men were hunters and women were gatherers.
- Used simple tools.
- Nomadic style of life was practised.
What are Paleolithic vegetables?
Ancient Veggies Were Small, Unpalatable Ancient tomatoes were the size of berries; potatoes were no bigger than peanuts. Corn was a wild grass, its tooth-cracking kernels borne in clusters as small as pencil erasers. Cucumbers were spiny as sea urchins; lettuce was bitter and prickly.
What is the agricultural theory of language diffusion?
The Agricultural Theory is the spread of culture that diffused the Proto-Indo-European language through Europe. This meant that the source area of the ancient language would have had to lie in an area of agricultural innovation.
Was Indo-European diffused by nomadic warriors or sedentary farmers?
Indo-European languages were spread not by marauding horsemen from the Caucuses but with the expansion of agriculture from Anatolia between 8000 and 9500 years ago.
What is the best example of the diffusion of a language?
The population divided and evolved into the four different languages, and then the disease spread. Which of the best example of the diffusion of a language? The spread of English via the Internet.
What hypothesis has Marija Gimbutas contributed to?
Marija Gimbutas (Lithuanian: Marija Gimbutienė, Lithuanian pronunciation: [‘ɡɪmbutas]; January 23, 1921 – February 2, 1994) was a Lithuanian archaeologist and anthropologist known for her research into the Neolithic and Bronze Age cultures of “Old Europe” and for her Kurgan hypothesis, which located the Proto-Indo- …
Who are Kurgan people?
Kurgan culture, seminomadic pastoralist culture that spread from the Russian steppes to Danubian Europe about 3500 Bc, . By about 2300 bc the Kurgans arrived in the Aegean and Adriatic regions. The Kurgans buried their dead in deep shafts within artificial burial mounds, or barrows.
How did the Kurgan theory spread?
In contrast to the Anatolian hypothesis, which defends that the diversification of PIE occurred some 8,500 years ago, when the first farmers from the Near East (currently Turkey) brought it to Europe, there is the Kurgan hypothesis, which proposes that the language was spread by nomadic herders of the steppes found to …
What is an example of conquest theory?
conquest theory One major theory of how Proto-Indo-European diffused into Europe which holds that the early speakers of Proto-Indo-European spread westward on horseback, overpowering earlier inhabitants and beginning the diffusion and differentiation of Indo-European tongues Example: car dealerships being close to each …
What is linguistic hearth?
Linguistic hypothesis proposing the existence of an ancestral Indo-European language that is the hearth of the ancient Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit languages which hearth would link modern languages from Scandinavia to North Africa and from North America through parts of Asia to Australia.
How did English become widely diffused?
How did English become widely diffused? English became diffused when England invaded and diffused to other countries. It also became diffused through England’s colonies. … England diffused to North American in the 1700s when settlers began to build colonies in North America.
Is Chinese an Indo-European language?
Old Chinese borrowed hundreds of words from Tocharian, and all of the languages that Old Chinese evolved into (Mandarin, Cantonese, Shanghainese, Hakka) inherited those words. So, in other words, Chinese languages did have Indo-European influence.
Is Latin a proto language?
Some universally accepted proto-languages are Proto-Indo-European, Proto-Uralic, and Proto-Dravidian. … For example, Latin is the proto-language of the Romance language family, which includes such modern languages as French, Italian, Portuguese, Romanian, Catalan and Spanish.
Is Arabic Indo-European?
Well, for starters, because Arabic is not an Indo-European language. It’s a Semitic language, like Hebrew, Aramaic, Amharic, Tigrinya, Soqotri, and Akkadian, among others.
Who first proposed the Indo-European hypothesis?
The tale begins with linguists in the late 1700’s, in particular, William Jones, a British judge who lived in India and in 1786 was the first person to suggest the possibility of Indo-European civilization. Jones’ hypothesis opened a new door to the past and sparked the modern science of historical linguistics.
How does the Anatolian hearth theory say the Indo-European family originated and diffused?
5-10: In the Anatolian hearth theory, Indo-European originated in Turkey before the Kurgans and diffused through agricultural expansion. Fig. 5-11: Distribution of the world’s main language families. Languages with more than 50 million speakers are named.